Wavelength Chart
Wavelength Chart - Wavelength, distance between corresponding points of two consecutive waves. “corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. The wavelength of light is defined as “the distance between the two successive crests or troughs of the light wave”. In other words, it is the length of. The wavelength of a wave describes how long the wave is. It is denoted by the greek letter lambda (λ).
“corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. Alternately, we can measure from. These repeating patterns known as wavelengths are represented by the letter lambda (λ). Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The distance from the crest (top) of one wave to the crest of the next wave is the wavelength.
The wavelength is a property of a wave that is the distance between identical points between two successive waves. “corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. The wavelength of a specific wave is the distance over which a wave repeats, as shown in figure 1. Wavelength, distance between corresponding points of two consecutive.
In other words, it is the length of. Alternately, we can measure from. It is denoted by the greek letter lambda (λ). The wavelength of light is defined as “the distance between the two successive crests or troughs of the light wave”. [3][4] the inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency.
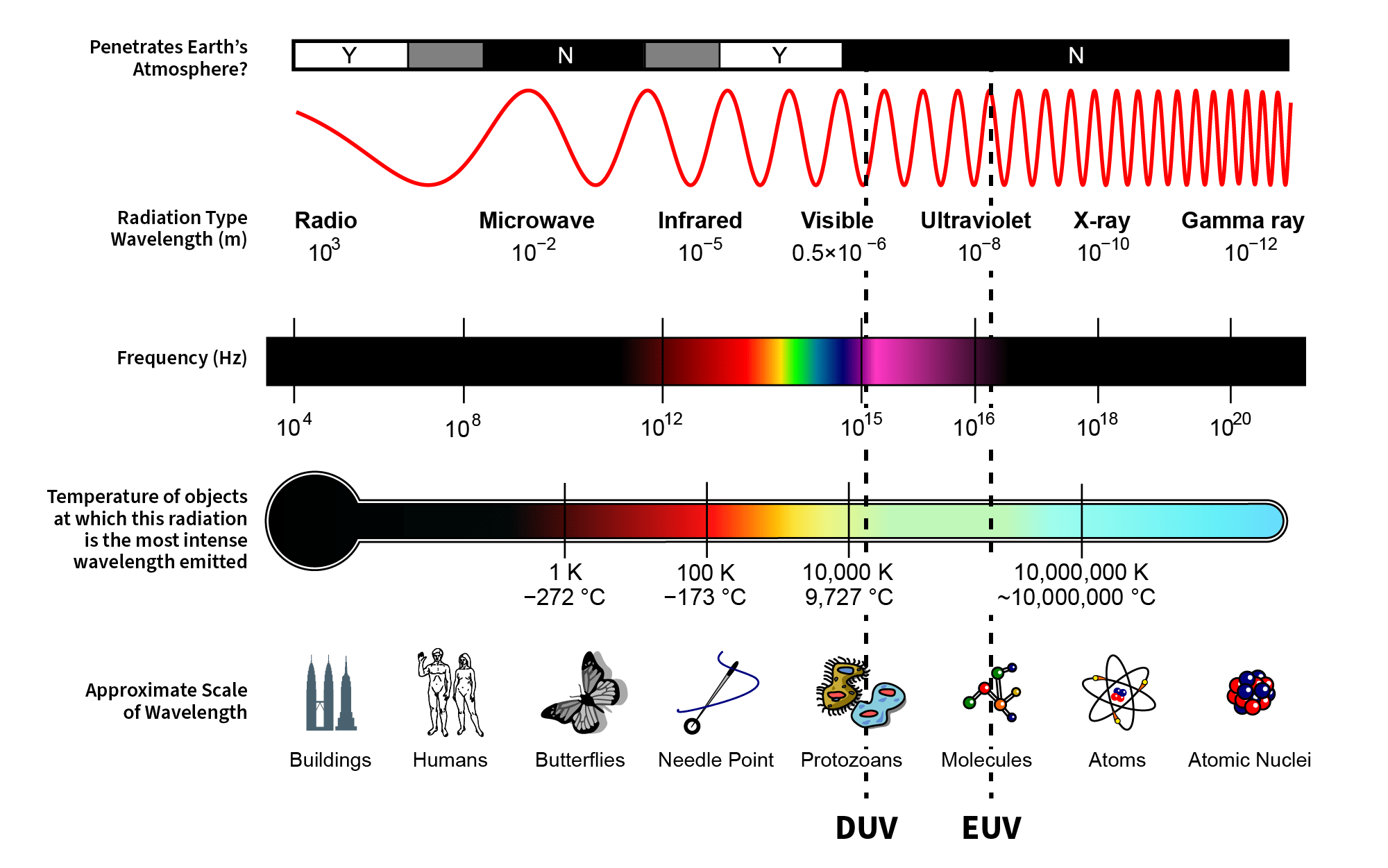
The distance between one crest (or trough) of one. The wavelength is a property of a wave that is the distance between identical points between two successive waves. In other words, it is the length of. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of..
The wavelength of a specific wave is the distance over which a wave repeats, as shown in figure 1. Wavelength (λ) refers to the distance between consecutive points of a sinusoidal wave that are in phase with each other. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum is the.
Wavelength (λ) refers to the distance between consecutive points of a sinusoidal wave that are in phase with each other. Alternately, we can measure from. These repeating patterns known as wavelengths are represented by the letter lambda (λ). [3][4] the inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. “corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same.
Normally this is done by measuring from peak to peak or from trough to. “corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies.
The wavelength is calculated by determining the distance between corresponding points on consecutive waves. Alternately, we can measure from. The wavelength is a property of a wave that is the distance between identical points between two successive waves. “corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. The wavelength of a wave describes how long.
“corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of. Wavelength, distance between corresponding points of two consecutive waves. Normally this is done by measuring from peak to peak or from trough.
Wavelength Chart - “corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. The distance from the crest (top) of one wave to the crest of the next wave is the wavelength. [3][4] the inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. The distance between one crest (or trough) of one. In other words, it is the length of. It is denoted by the greek letter lambda (λ). These repeating patterns known as wavelengths are represented by the letter lambda (λ). The wavelength of a wave describes how long the wave is. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of. Wavelength, distance between corresponding points of two consecutive waves.
Wavelength (λ) refers to the distance between consecutive points of a sinusoidal wave that are in phase with each other. The wavelength is a property of a wave that is the distance between identical points between two successive waves. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of. Alternately, we can measure from. Wavelength, distance between corresponding points of two consecutive waves.
Wavelength (Λ) Refers To The Distance Between Consecutive Points Of A Sinusoidal Wave That Are In Phase With Each Other.
Normally this is done by measuring from peak to peak or from trough to. “corresponding points” refers to two points or particles in the same phase—i.e., points that. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of. The wavelength of a specific wave is the distance over which a wave repeats, as shown in figure 1.
The Wavelength Of Light Is Defined As “The Distance Between The Two Successive Crests Or Troughs Of The Light Wave”.
The distance between one crest (or trough) of one. [3][4] the inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. The wavelength is calculated by determining the distance between corresponding points on consecutive waves. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns.
These Repeating Patterns Known As Wavelengths Are Represented By The Letter Lambda (Λ).
The wavelength of a wave describes how long the wave is. In other words, it is the length of. Alternately, we can measure from. The wavelength is a property of a wave that is the distance between identical points between two successive waves.
It Is Denoted By The Greek Letter Lambda (Λ).
The distance from the crest (top) of one wave to the crest of the next wave is the wavelength. Wavelength, distance between corresponding points of two consecutive waves.